News Details
What are the six axes of a six-axis robot, and what are their functions?
Release time:
2024-10-21 11:40
Industrial robots in production generally need to be equipped with peripheral devices in addition to their own performance characteristics, such as rotating tables for rotating workpieces and moving platforms for moving workpieces.
Industrial robots generally need to be equipped with peripheral devices in addition to their own performance characteristics, such as rotating workpiece turntables and moving workpiece platforms. The motion and position control of these peripheral devices need to be coordinated with the industrial robot and require corresponding precision. Typically, the robot's motion axes can be divided into robot axes, base axes, and tooling axes, with the base axes and tooling axes collectively referred to as external axes.
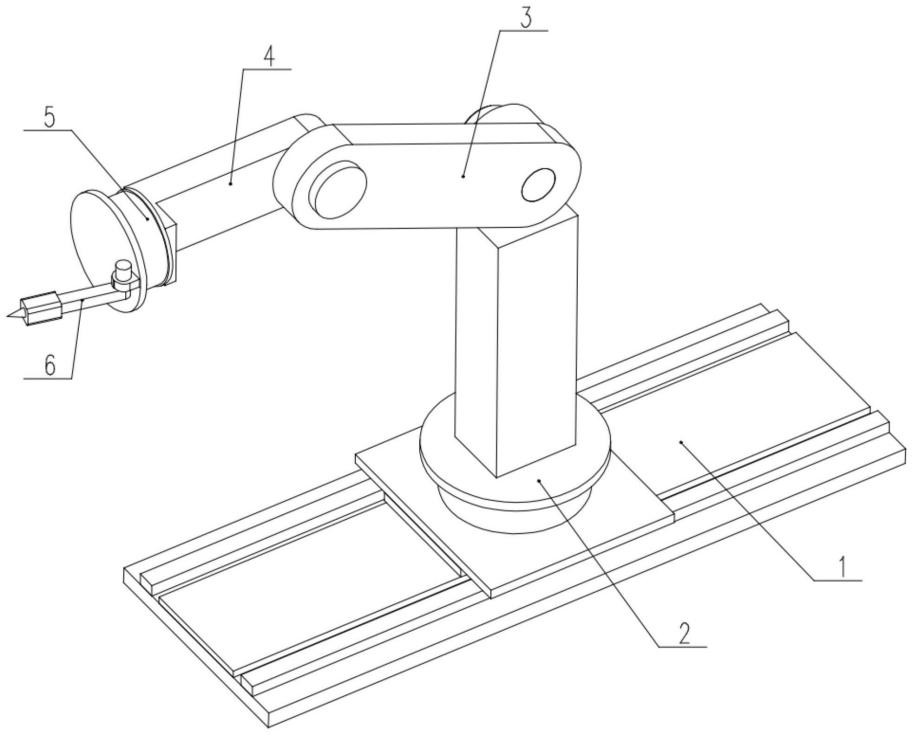
The six-axis industrial robot is a commonly used 6-joint industrial robot in actual production. It is referred to by various names such as six-axis robotic arm, six-joint manipulator, six-axis arm, etc. Industrial robots generally refer to four-axis, five-axis, and six-axis manipulators. Each robot's joint structure may vary; below we will explain which six axes make up a six-axis robot and their functions.
First axis: The main body rotation axis, which connects to the base, is the axis that bears a significant load for the industrial robot. It can rotate left and right, similar to the action of a grinding disc, supporting the entire weight of the robot and allowing for significant lateral swinging.
Second axis: The main arm's forward and backward swing axis is the core connection point of the robot components, serving as an important axis for controlling the forward and backward swinging and extension of the robot.
Third axis: The third axis controls the forward and backward swinging of the robot. Its function is similar to that of the second axis, also controlling the up-and-down loading and unloading function of the robot. The movement range of the third axis is relatively small; however, this also contributes to the extended reach of the six-axis robotic arm.
Fourth axis: This is the position of the cylindrical tube on top of the industrial robot that can rotate freely. It is essentially a rotating cylinder with an internal cable restriction. The fourth axis controls a 180° free rotation of the upper arm section, equivalent to a human's forearm.
Fifth axis: The fifth axis is very important. Once you have roughly adjusted your position, you need to precisely locate it on the product using this axis. This position corresponds to the wrist joint in a human arm, allowing for small up-and-down movements. It enables flipping actions for products or fixed tools after they are grasped.
Sixth axis: The end rotation axis is a joint used for fine-tuning positions at the back; after you have positioned the fifth axis on the product, if minor adjustments are needed, you will use the sixth axis. The sixth axis acts like a turntable that can rotate horizontally 360°, allowing for more precise positioning on the product.
Related News
What are the typical application scenarios of industrial robots?
Automobile manufacturing: Industrial robots are widely used in the automobile manufacturing process, including tasks such as welding, assembly, painting, dispensing, and inspection.
What are the operating procedures and precautions for welding robots?
A welding robot is an industrial robot that has welding programs preset in its control system, allowing the robot to automatically complete welding tasks.
What are the classifications of welding robots?
The types of welding robots are divided into spot welding robots, arc welding robots, laser welding robots, etc. The most common ones in the market are spot welding robots and arc welding robots.
Current status and development trends of welding robots!
Welding robots are robots that can autonomously perform welding tasks, and they play a crucial role in industrial production.