News Details
Industrial Robot Industry Research Report
Release time:
2019-07-24 00:00
Industrial robots refer to multi-degree-of-freedom robots used in the industrial field. The industrial robot industry chain mainly consists of upstream core components, midstream industrial robot body assembly, and downstream system integration.

Image source @ Vision China
Overview of the Industrial Robot Industry Development
In 1954, the concept of industrial robots was first proposed by Devol in the United States, and a patent was applied for. The key point of this patent is to control the robot's joints using servo technology and to teach the robot actions through human hands, allowing the robot to record and reproduce movements. This is known as a teach-and-replay robot. Most existing robots use this control method.
In 1959, the first industrial robot from UNIMATION was born in the United States, marking a new era in robot development. Its mechanical structure also became a template for the industry. Later, UNIMATION was acquired by Swiss STAUBLI, which further improved and developed it using STAUBLI's technological advantages. The first robot in Japan was imported from UNIMATION by KAWASAKI and was imitated and improved by Kawasaki for domestic promotion.
Industrial robots refer to multi-degree-of-freedom robots used in industrial fields. The industrial robot industry chain mainly consists of upstream core components, midstream assembly of industrial robot bodies, and downstream system integration. Among them, controllers, servo systems, and precision reducers are the most important core components of robots.
The industrial robot industry is crucial for China, with a market space of up to hundreds of billions across the entire industry chain. Its application spans various sub-sectors of manufacturing, playing an important role in the transformation and upgrading of China's manufacturing industry and promoting rapid development in other industries.
In the industrial robot industry chain, the core technology and challenges are concentrated among upstream manufacturers, specifically in the production of core components. Costs and profits are also concentrated in this area, with core component costs accounting for over 70% of the entire robot body. Therefore, whoever masters the production technology and capability of core components occupies the highest point in the robot industry and holds significant pricing power.
Currently, in China's industrial robot market, the supply of upstream core components is mostly occupied by foreign manufacturers. Domestic manufacturers mainly focus on midstream assembly of robot bodies and downstream system integration, undertaking low-value-added work such as secondary system development, custom parts, and after-sales service. This results in foreign manufacturers capturing the industrial dividends brought by China's vast market potential.
Foreign industrial robot giants are themselves providers of core components; thus, they have inherent cost advantages and technological advantages regarding component costs. Additionally, they often secure favorable procurement prices through large purchase volumes and exclusive agreements. In contrast, domestic small and medium-sized enterprises often have to purchase reducers at nearly three times the price charged by foreign manufacturers and servo motors at nearly double the price.
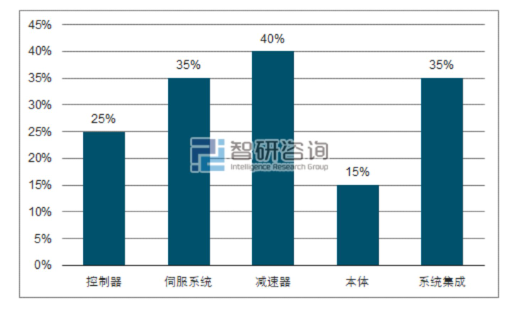
Cost composition of industrial robots and gross profit margin of the industry chain; data source: public information, organized by Zhiyan Consulting
With the development of China's manufacturing industry, especially the rapid growth of the automotive and motorcycle parts manufacturing industries, the assembly volume of industrial robots will steadily increase. Furthermore, the expansion of China's construction industry, mining industry, railways and public construction, hydropower engineering construction, as well as construction machinery markets will also promote the industrial robot sector.
The structural components of construction machinery are mostly welded parts. To improve welding quality and efficiency to meet market demands, many engineering machinery manufacturers are now requiring robots for welding.
Current Status and Trends of the Industrial Robot Industry
Since 2009, global annual sales of industrial robots have been increasing year by year. In 2017, global inventory of industrial robots reached 1.946 million units, expected to reach 2.327 million units in 2018. In 2017, global sales of industrial robots were as high as 285 thousand units. The International Federation of Robotics also predicts that global annual sales of industrial robots will maintain a growth rate close to 15% over the next three years.
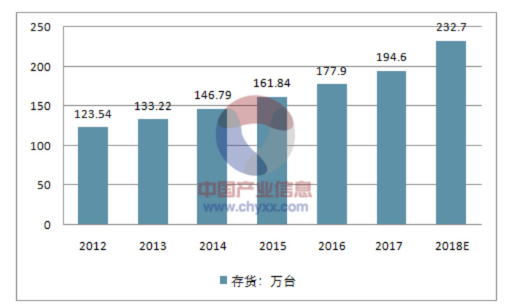
2012-2018 Global Industrial Robot Inventory Trends; data source: China Industry Information Network
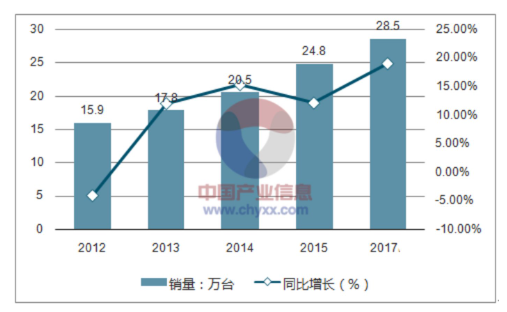
2012-2017 Global Industrial Robot Sales and Year-on-Year Growth; data source: China Industry Information Network
The Four Major Families of Industrial Robots:
1. Japan's FANUC
FANUC is a Japanese company specializing in CNC systems established in 1956. It is the world's largest manufacturer of professional CNC systems, holding a global market share of 70%. FANUC first launched an electro-hydraulic stepping motor in 1959 and gradually developed a hardware-based open-loop CNC system over subsequent years.
Since FANUC's first robot was introduced in 1974, FANUC has been committed to leading innovation in robotics technology. It is the only company in the world that uses robots to make robots and provides integrated vision systems for its robots; it is also unique in offering both intelligent robots and intelligent machines.
In June 2008, FANUC became the world's first manufacturer to exceed an installed base of 200 thousand robots; by 2011, FANUC's global installed base had surpassed 250 thousand units with a stable market share at first place.
2. Switzerland's ABB (Asea Brown Boveri)
ABB is a Swiss-Swedish multinational company headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland. Founded in Europe in 1988, it entered China in 1994 and established ABB China Limited in 1995. Since 2005, ABB's production, R&D, and engineering centers for robotics have begun relocating to China; currently, China has become ABB's largest global market.
ABB Group operates in over 100 countries worldwide with approximately 145 thousand employees; its global sales revenue was about $40 billion in 2014 with sales revenue in China around $5.8 billion. ABB has comprehensive business activities including R&D, manufacturing, sales, and engineering services in China with about 19 thousand employees. It has established 38 subsidiaries and over 100 offices across mainland China.
ABB's robotic products and solutions have been widely applied across various industries such as automotive manufacturing, food & beverage processing, computers & consumer electronics for different operational processes including welding, assembly, handling, spraying, finishing, packaging, and palletizing.
3. Japan's YASKAWA
YASKAWA Electric Corporation was founded in 1915 and is headquartered in Kitakyushu City, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. In April 1999, YASKAWA Electric (China) Co., Ltd was registered in Shanghai with a registered capital of $31.1 million; its office is located on the twelfth floor of Hongxiang Building at No.21 Huanghe Road Shanghai City. In July 2012, YASKAWA's first overseas robot production base was established in Changzhou Wujin High-tech Zone; this base will produce dissolving robots used for automotive-related manufacturing with state-of-the-art equipment.
The total project investment is approximately $300 million with a designed capacity of producing 12 thousand sets of robots per year (including control systems) with annual sales expected to reach RMB600 million. The base commenced production in June 2013. In 2015 YASKAWA launched ReWalk - a 'robot that assists spinal cord injury patients walk', bringing hope to those affected.
ReWalk, as an exoskeleton robot, does not use force sensors and electromyography sensors, but instead employs an innovative computational algorithm that can locate the wearer's center of gravity to achieve natural walking and ease of wear. It has been commercialized in Europe and the United States and can help patients with lower limb paralysis caused by spinal cord injuries to stand and walk.
Patients can use it in daily life after receiving training at designated hospitals (20 hours of basic training and a minimum of 20 hours of application training).
4. KUKA from Germany
KUKA is a leading manufacturer in the field of industrial robots and automatic control systems, headquartered in Augsburg, Germany. KUKA Robotics has over 20 subsidiaries worldwide, most of which are sales and service centers. KUKA operates in the United States, Mexico, Brazil, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, India, and various European countries.
KUKA Robotics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of KUKA in China, established in 2000. It is the first and only overseas factory set up by KUKA outside Germany. KUKA Robotics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. is located in Shanghai. The brand ambassador for KUKA Robotics is table tennis player Timo Boll.
In 2015, KUKA launched its first lightweight industrial robot LBR iiwa, which features a groundbreaking design with a 7-axis robotic arm. Its high sensitivity, flexibility, precision, and safety make it particularly suitable for industries requiring flexibility and precision (such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, precision instruments, etc.), meeting more operational needs in industrial production.
Analysis of the current situation of China's industrial robot industry
China's industrial robots began to take off in the 1980s with the 'Seventh Five-Year' technology breakthrough initiative. With national support through the 'Seventh Five-Year' and 'Eighth Five-Year' initiatives, China has now basically mastered the design and manufacturing technology of robotic manipulators, control system hardware and software design technology, kinematics and trajectory planning technology. Some key components for robots have been produced, and robots for painting, arc welding, spot welding, assembly, handling, etc., have been developed; among them, over 130 painting robots have been applied on nearly 30 automatic painting production lines in more than twenty enterprises.
However, overall, China's industrial robot technology and its engineering application level still lag behind foreign countries. For example: reliability is lower than that of foreign products; the application engineering of robots started relatively late with a narrow application field; there is a gap between production line system technology and that of foreign countries.
From 2013 to 2017, China's industrial robot sales achieved rapid growth, ranking first in the world for several consecutive years. Since 2013, China has become the largest market for industrial robots globally. In 2016, sales were approximately 87,000 units, accounting for 30% of the global market share, close to the combined sales of Europe and North America. The domestic manufacturing industry's demand for 'machine substitution' is strong; it is expected that industrial robot sales will continue to grow rapidly.
Data shows that from 2017 to 2020, China's industrial robot sales will increase from 115,000 units to 210,000 units, with an average annual growth rate of about 25%, and its global market share will rise from 33% to 40%. As the trend of upgrading and transforming China's manufacturing industry becomes increasingly evident, the trend of machine substitution provides ample market space for the industrial robot industry. In 2017, China's industrial robot sales increased to 138,000 units, making it the global leader in industrial robot sales for five consecutive years.

In 2017, China's industrial robot sales reached 138,000 units. Source: Public data compilation.
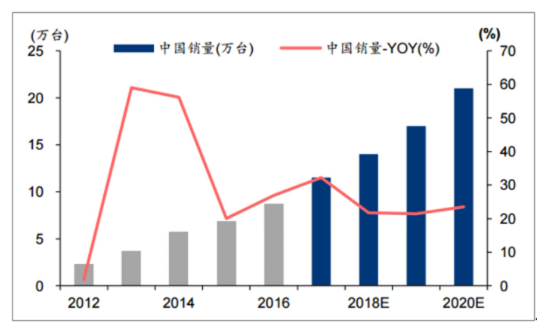
From 2017 to 2020, China's industrial robot sales growth rate is expected to be around 25%. Source: Public data compilation.
The International Federation of Robotics predicts that by 2020 China's industrial robot sales will exceed 210,000 units. China has been the largest consumer market for industrial robots globally for five consecutive years. The Chinese industrial robot market is entering an accelerated growth phase; the International Federation of Robotics predicts that future sales growth will maintain around 20%.
China's industrial robot sales are expected to maintain a growth rate of around 20%. Source: Public data compilation.
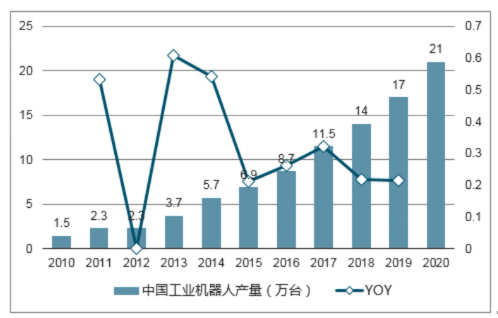
According to data analysis from public sources: In 2017 China's industrial robot output was at 138,000 units with domestic brand sales accounting for about 32.8%. Assuming that by 2020 domestic brand output reaches a share of 50%, then the output in that year would be approximately 200,000 units. Thus we can calculate that from 2017 to 2020 the CAGR for industrial robot output would be approximately at 15.12%, estimating outputs for each year as follows: 1509/1737/2000 units respectively.
In 2016 China's industrial robot density was at a rate of 68 units per ten thousand people. According to data from the National Bureau of Statistics: In that year China produced approximately 72,400 units; thus based on density targets it is estimated that output will reach about 159700 units by the year of2020. This leads us to calculate that from2017-2020 CAGR for output would be around6.8%, estimating outputs as follows:14000/14950/15970 units respectively.
Using China's industrial robot output estimates from2018-2020 at150/170/200 thousand units as a baseline with an average price per unit at150 thousand yuan; it estimates that by2020the market space will reach30 billion yuan.
However among China's total sales of138000units inindustrial robots; foreign brands occupy a significant majority share of themarket; while domestic self-branded robots have seen an increase in sales their overall share remains relatively small.
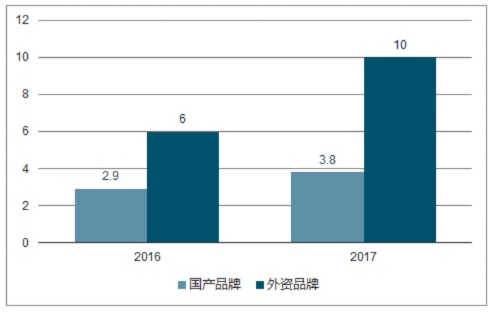
In2017China'sindustrialrobotmarketwasstillmainlydominatedbyforeignbrands.Source:Publicdatacompilation.
1.Foreign-funded robots drive rapid market development
According to preliminary statistics from CRIA and IFR: In2017China'sindustrialrobotmarketcontinuedtogrowwithtotalannualsalesof141000units,a year-on-year increaseof58.1%,settingahighrecordforgrowthrate.Inthatyeardomesticrobotsaleswere37800units,a year-on-year increaseof29.8%;foreign-fundedrobotsaleswere103000unitswithayear-on-yeargrowthrateof71.9%.
Comparedto last year,the growth rateofdomesticindustrialrobotssalesremainedbasicallystablewhileforeignbrandsalesgrowthrateobviouslyaccelerated.Foreignfundedrobotsaccountedfor73.2%oftotalmarketvolume,increasingby5.9percentagepointscomparedtothepreviousyear.
2.Multi-joint robots became the main model for domestic robots for the first time
Fromtheperspectiveofmechanicalstructure,in2017multi-jointrobotsrankedfirstinvariousrobottypesinChinamarketwithannualsalesexceeding91000units,a year-on-year increaseof66.6%,andthegrowthratewasalsoobviouslyaccelerated;amongthem domestic multi-jointrobotssawremarkablesalesperformancewithsalesfirst surpassingcoordinate-type robotsbecomingtheprimarymodelwithannualcumulativesalesreaching16000units,a year-on-year increaseof35.5%.
However,due to acceleratedsalesofforeignmulti-jointrobots,theproportionofdomesticmulti-jointrobotsinthesametypeofrobotmarketfellfrom21.5%in2016to17.5%.
The total sales of coordinate robots exceeded 21,200 units, with a year-on-year growth of 15.4%, accelerating compared to the previous year. SCARA robots had the highest growth rate among various models, with sales doubling. The sales of parallel robots saw a year-on-year decline for the first time since 2013, with a decrease of 3%.
3. Handling and loading/unloading remain important areas driving rapid growth in the Chinese robot market.
From the perspective of application fields, handling and loading/unloading are still the primary application areas in the Chinese market, with sales exceeding 63,000 units in 2017, a year-on-year increase of 57.5%, showing a significant rebound compared to the previous year, remaining consistent with total sales in 2016. Sales of welding and brazing robots reached 35,000 units, up 56.5% year-on-year, with a substantial increase in growth rate. Sales of assembly and disassembly robots reached 28,000 units, up 71.2%.
In addition, sales of processing robots achieved exponential growth, but due to a small base, their overall impact is not significant. Overall, in 2017, sales of various types of robots in the Chinese market increased, mainly driven by handling and loading/unloading robots.
It is expected that from 2017 to 2020, the domestic market size for robot bodies will grow from 27.2 billion yuan to 42.7 billion yuan. There are many types of industrial robots; depending on their application functions and technical performance, the price per unit varies greatly, ranging from hundreds of thousands to millions of yuan. Based on the global average price of industrial robots and assuming an annual price reduction of 5% (due to mass production and technological advancements), it is estimated that the sales revenue for China's industrial robot bodies will be 27.2 billion yuan, 31.5 billion yuan, 36.4 billion yuan, and 42.7 billion yuan respectively from 2017 to 2020, with an average annual growth rate of about 18%.
Significant characteristics of industrial robots.
1. Programmable. The further development of production automation is flexible startup. Industrial robots can be reprogrammed according to changes in their working environment; therefore, they can perform well in flexible manufacturing processes that require balanced high efficiency for small batch and diverse varieties and are an important component of flexible manufacturing systems.
2. Human-like features. Industrial robots have mechanical structures similar to human walking, waist rotation, upper arms, forearms, wrists, claws, etc., and are controlled by computers. In addition, intelligent industrial robots have many human-like 'biological sensors', such as skin-type contact sensors, force sensors, load sensors, visual sensors, auditory sensors, language functions, etc. These sensors enhance the adaptability of industrial robots to their surrounding environment.
3. Versatility. Apart from specially designed dedicated industrial robots, general industrial robots have good versatility when performing different tasks. For example, changing the end effector (claw or tool) of an industrial robot allows it to perform different tasks.
4. Comprehensiveness. The technology involved in industrial robotics covers a wide range of disciplines; it can be summarized as a combination of mechanics and microelectronics - mechatronics technology. Third-generation intelligent robots not only have various sensors for acquiring external environmental information but also possess memory capabilities, language comprehension abilities, image recognition capabilities, reasoning and judgment abilities related to artificial intelligence; all these are closely related to the application of microelectronics technology, especially computer technology.
Therefore, the development of robot technology will inevitably drive the development of other technologies; the level of development and application of robot technology can also verify a country's level of scientific and technological advancement as well as industrial technology.
Technological trends in the industrial robot industry.
Currently, industrial robot technology is being developed towards directions such as fuzzy control, intelligence, versatility, standardization, modularization, high precision, networking as well as self-improvement and self-repair capabilities.
First of all, fuzzy control is a control method that utilizes the basic ideas and theories of fuzzy mathematics. For complex systems with too many variables where traditional control models struggle to accurately describe system dynamics, fuzzy mathematics can be used to address these control issues. The future characteristics of robots lie in their higher intelligence.
With continuous advancements in high-tech fields such as computer technology, fuzzy control technology, expert system technology, artificial neural network technology and intelligent engineering technology etc., the working capabilities of industrial robots will see breakthrough improvements and developments.
Secondly, achieving generalization, standardization and modularization for components and parts of industrial robots is one important way to reduce costs.
Thirdly, as manufacturing industries demand more from robots, developing high-precision industrial robots is an inevitable outcome.
Fourthly, most currently applied robots have only achieved simple network communication and control; how to evolve robots from independent systems into collective systems for remote operation monitoring and maintenance is one current hot topic in robot research.
Finally, robots should possess self-repair capabilities to better avoid production stoppages caused by unexpected situations. When erroneous instructions occur they should be able to alert or debug themselves; when components are damaged they should be able to repair themselves.
Relevant policies regarding the industrial robot industry in China.
1. National policy support.
Since the 1990s, the central government has increased investment in R&D for industrial robots; under the National High Technology Research and Development Program (the '863 Program'), key support has been given for research on vision systems and control theories/methods as well as intelligent robot R&D across multiple fields including assembly systems. After 2010, various government departments including the State Council and Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued policies promoting transformation and upgrading in manufacturing industries while developing intelligent equipment industries.
In 2012, strategic emerging industries and high-end equipment manufacturing development '12th Five-Year Plan' was introduced along with special plans for intelligent manufacturing science and technology development during '12th Five-Year Plan', establishing special funds for intelligent manufacturing equipment development aimed at supporting key intelligent components like welding processing through guiding local governments and socialized funding; projects were allocated R&D subsidy funds after passing review.
For example, in 2014 listed company Robot (stock code: 300024) had its digital production workshop project included in special funding with a proposed subsidy amounting to 20 million yuan accounting for about 20% of total project development costs. In December 2013 the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued guidelines for promoting industrial robot industry development increasing financial support for key technologies like servo drives while supporting R&D and commercialization in key intelligent components fields.
In 2015 'Made in China 2025' listed robotics as one of ten key areas; in 2016 'Robot Industry Development Plan (2016-2020)' clearly outlined tackling key technologies for industrial robots focusing on breaking through technical barriers for five key components: reducers; dedicated servo motors/drives; controllers; sensors; end effectors while developing ten types including arc welding robots and fully autonomous programming intelligent industrial robots.
In December 2016 the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology formulated 'Industrial Robot Industry Normative Conditions' strengthening quality management for industrial robot products while setting requirements for production enterprises manufacturing robot bodies as well as integrated application enterprises based on comprehensive conditions enterprise scale quality requirements R&D innovation capabilities talent strength etc.
Specific national policies are as follows:
Implementation time: Year 2012
National department: State Council
'12th Five-Year Plan' Development Plan for High-end Equipment Manufacturing
Content introduction: Clearly state that financial and tax policy support for intelligent manufacturing will be strengthened. Increase investment in the research and development of technologies and devices such as servo drive devices, promote system integration and complete sets. Focus on supporting the research and development, industrialization, and application promotion of intelligent technology, intelligent measurement and control devices and components, and major intelligent manufacturing complete equipment.
Implementation time: Year 2012
National Department: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology
Name of the law and regulation: Development Plan for Intelligent Manufacturing Equipment Industry during the 12th Five-Year Plan
Content introduction: Industrial robots, overcoming common technologies of core components such as industrial robot bodies, precision reducers, servo drives, motors, and controllers, independently developing engineering products for industrial robots to achieve technological breakthroughs and industrialization of industrial robots and their core components.
Implementation time: 2015
National department: State Council
Name of the law and regulation: Made in China 2025
Content introduction: The Chinese version of the 'Industry 4.0' plan was announced by the State Council in May 2015. The plan proposes a 'three-step' strategy for building a strong manufacturing country in China over three decades, serving as the action program for the first decade.
Implementation time: 2016
National Departments: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Finance
Name of the law and regulation: Robot Industry Development Plan (2016-2020)
Content introduction: The plan proposes a five-year overall goal for industry development: to form a relatively complete robot industry system. The technological innovation capability and international competitiveness will be significantly enhanced, product performance and quality will reach the international level of similar products, major breakthroughs will be achieved in key components, basically meeting market demand. Specific goals are proposed from four aspects: continuous growth of industry scale, significant improvement in technology level, major breakthroughs in key components, and significant achievements in integrated applications.
2. Local government support
As domestic labor costs continue to rise, enterprises have a strong demand for 'replacing humans with machines', promoting the development of the robot industry. A market survey by the Chinese Academy of Engineering shows that among surveyed enterprises, 64.2% have a strong willingness to do so, with 14.5% preparing for 'replacing humans with machines'. Currently, China has only 36 robots per ten thousand manufacturing workers, which is just one-tenth of that in Germany and Japan, indicating a huge potential demand.
Local governments strongly support 'replacing humans with machines'. Regions such as Guangdong, Zhejiang, Shanghai, Hubei, Heilongjiang have introduced relevant financial subsidy policies to support the application of industrial robots. Among them, Guangdong Province has allocated special funds for robot development within its 'Special Fund for Industrial and Information Technology Development', with an allocation of 360 million yuan in 2016 to provide a certain percentage of procurement price subsidies. The Shenzhen municipal government invests 500 million yuan annually in special funds to subsidize intelligent industries such as robots; Dongguan municipal government provides a subsidy of 15% for enterprises purchasing domestic robots, with town-level subsidies ranging from 20%, 30%, to 50%. In Zhejiang Province, provincial finance has cumulatively arranged nearly 600 million yuan to support 'replacing humans with machines' technological transformation and has introduced an industrial robot purchase reward subsidy policy with a provincial-to-local matching ratio of 1:2, providing a subsidy of 10% on the purchase price of industrial robots.
3. Participation of private capital
Numerous funds related to the robot industry have emerged. Localities such as Shenyang, Shanghai, Dongguan, Qingdao have successively established industrial funds. According to information from Tianjin Net, in order to accelerate the gathering of global resources for intelligent manufacturing and seize opportunities in the intelligent technology industry, the Binhai New Area government, China Communications Construction Group Co., Ltd., Bohai Bank, Beijing Xinghe World Group Co., Ltd., etc., jointly initiated the establishment of an intelligent technology industry mother fund with a total scale of 30 billion yuan; the Changsha municipal government established the Changsha Intelligent Manufacturing Industry Investment Fund together with Qianhai Capital Group, Fengyun Capital, Huamin Capital, etc., with a scale of 10 billion yuan.
Analysis of competition among industrial robot companies
1. Domestic market competition status
According to a report by Zhongtou Consulting titled 'Investment Analysis and Prospect Forecast Report on China's Robot Industry (2016-2020)', robots have attracted public attention in China due to the urgent need for transformation faced by manufacturing industries in recent years. They are expected to replace labor force and enhance manufacturing as well as industrial levels. The robot market is dominated by four international giants (Switzerland's ABB, Japan's Fanuc Corporation, Japan's Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Germany's KUKA Robotics), while domestic robots have low technical content and high usage and maintenance costs.
Many traditional manufacturing enterprises represented by Gree and Midea Group have invested in purchasing or independently developing intelligent equipment to cope with rising labor costs through 'replacing humans with machines'.
In contrast, small and medium-sized enterprises usually only have the capacity to purchase while large enterprises can invest in research and development. Regional benchmark enterprises like Gree and Midea typically go further under government guidance: making huge investments to capture market share.
Taking Shunde, where the robot industry is developed as an example, in the first half of 2015 there were investments from Yaskawa Electric Corporation amounting to 1 billion yuan collaborating with Midea on motor robot projects; Switzerland's ABB engaged in technical cooperation with Lixunda; Germany's KUKA built an engineering center in the Sino-German Industrial Service Zone; Japan's Kawasaki Heavy Industries collaborated with Longshen to establish a robot training center.
The entry of international robot giants has also driven more than ten robot projects such as Keda high-pressure line robots to settle down. With many robot projects established, Shunde had 57 large-scale industrial enterprises promoting robot applications in the first half of the year.
2. Enterprises increase investment
On August 4th, 2015, Midea announced its robot industry strategy and jointly established two subsidiaries with Japan's Yaskawa Electric Corporation. The two subsidiaries focus on industrial robots and service robots respectively.
Among them, Guangdong Yaskawa Midea Industrial Robot Co., Ltd., has a total investment of 200 million yuan with registered capital of 100 million yuan; Midea holds a cash contribution accounting for 49% of registered capital. Guangdong Midea Yaskawa Service Robot Co., Ltd., also has a total investment of 200 million yuan with registered capital of 100 million yuan; Midea holds a cash contribution accounting for 60.1% of registered capital.
On the same day, Gree opened its automated production workshop for reporters at the first West Pearl River Advanced Equipment Manufacturing Investment Trade Fair and publicly showcased its latest progress in self-developed robots. Gree aims to achieve world-leading levels in equipment manufacturing within five years. On the stamping automation line at its sheet metal spraying branch factory, rows of orange six-axis robots are neatly arranged flexibly moving their 'arms' to grab components.
These six-axis robots come from Switzerland's ABB Group; however, this production line composed of robots and related equipment is designed and developed independently by Gree. The core content of this entire integration solution is done by Gree itself.
Since implementing 'replacing humans with machines' in 2011, Gree has successively established departments such as an automation office, automation technology research institute, automation equipment manufacturing department among others; it has about 2000 production and research personnel across its automation research production departments. Gree aims to achieve world-leading levels in equipment manufacturing within five years.
Currently, Gree has independently developed nearly 100 types of automated products covering more than ten fields including industrial robots, intelligent AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), injection molding manipulators, large automated production lines etc., holding more than twenty design patents. As of December 31st, 2014, the automation equipment manufacturing department had produced a total output of equipment amounting to1660 units and tooling amounting to1482 sets.
The main industrial robot manufacturers in China are companies such as Siasun, Estun, Efort, Xinsida, Tosida, and Guangzhou CNC; among them, Siasun, Estun, and Tosida have an annual production capacity of over 9,000 units, and Xinsida has a new factory under construction with an annual capacity of 10,000 units.
Industry competition barriers
1. Monopoly of international enterprise shares
The report shows that in 2016, the 'Big Four' of industrial robots—FANUC, ABB, Yaskawa, and KUKA—accounted for 58% of the global market share. Other internationally renowned brands also hold more than 4% of the global market share. In contrast, domestic robots have a relatively low global market share of only 9.7%.
The situation is similar domestically; in the same year, the 'Big Four' accounted for 57.4% of the domestic market share, while domestic brands only accounted for about 32.8%. However, compared to 25% in 2015, domestic brands have made significant progress. According to the national 'Robot Industry Development Plan (2016-2020)', the goal is to reach an annual production capacity of 100,000 units for domestic brand industrial robots and over 50,000 units for six-axis and above robots between 2017 and 2020. If this goal is successfully achieved, it would mean a compound annual growth rate of 37% for domestic brand industrial robot sales during this period.
2. Lack of core components
The servo system is the main power source for industrial robots and consists mainly of three parts: servo motors, servo drives, and encoders. The term 'servo' means 'to follow', referring to the control that follows position, speed, or torque according to command signals. Currently, the servo systems used in China's industrial robots are mainly monopolized by foreign brands, with Japanese brands accounting for about 50%, European and American brands for 30%, and Taiwanese brands and mainland companies only accounting for 10%.
Japanese companies include Yaskawa, Mitsubishi, Sanyo, Omron, Panasonic, etc., mainly focusing on small and medium power products; European and American companies include Siemens, Bosch Rexroth, Schneider Electric, etc., which have an advantage in large servos; domestic companies mainly include Inovance, Delta Electronics, Estun, etc., focusing on small and medium servos.
Overall, there is still a gap between China's servo motors and those from Japan and Europe/America. This gap is mainly reflected in: a lack of high-power products, insufficient miniaturization, unstable signal connectors, and a lack of high-precision encoders. These are also the main directions that domestic servo systems need to tackle in the future.
Industry SWOT analysis
1. Favorable factors affecting industry development:
① Support from domestic industrial policies
In April 2016, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), and Ministry of Finance jointly issued the 'Robot Industry Development Plan (2017-2021)'. The plan proposes to form a relatively complete robot industry system in China within five years and lists specific key tasks: first is to promote major landmark products to break through; second is to vigorously develop key components for robots; third is to strengthen industrial foundational capabilities; fourth is to actively promote application demonstrations; fifth is to cultivate leading enterprises.
The Chinese robot industry is at a stage where opportunities are overlapping due to the release of demand for industrial transformation and upgrading, prominent national policy dividends, and capital market support. There is huge investment potential in the upstream components of the robot industry chain, midstream manufacturing of bodies and system integration, and downstream application fields.
② Rapid development of collaborative robots
At the 19th China International Industry Fair in November 2017, various exhibitions and technology displays in the robotics field conveyed several new trends in industry development: miniaturization, lightweight design, and collaborative robots are becoming new trends in industrial robot development. Small and medium-sized enterprises leveraging collaborative robots are becoming an important driving force for rapid growth in the industrial robot market; human-machine collaboration will more accurately support intelligent manufacturing.
In 2016, China sold approximately 2,300 collaborative robots with a year-on-year growth of 109.09%; the market size reached 360 million yuan. From 2014 to 2016, China's sales volume and market size for collaborative robots had compound annual growth rates of 95.79% and 68.94%, respectively.
③ Demand for industrial upgrading from downstream manufacturing enterprises
Many manufacturing enterprises in developed countries have already achieved refined production processes that utilize automated equipment throughout production, inspection, warehousing, and packaging to ensure product stability and reliability. In contrast, most manufacturing enterprises in China are still at an early stage of automation with a focus on extensive development models that yield low product added value; there remains significant room for improvement in product stability.
As people's demands for product quality increase in the future, China's industrial manufacturing will also move towards intensive and intelligent directions for industrial upgrading. The degree of automation will continue to rise gradually along with increasing demand for automated equipment.
2. Unfavorable factors affecting industry development:
① Need to strengthen independent innovation capabilities
Although China has basically mastered relevant technologies related to body design manufacturing, control system software/hardware development, motion planning etc., there remains a significant gap compared to foreign countries regarding overall technical levels; China lacks original achievements and innovative concepts in core and key technologies; issues related to enterprise- and market-oriented demands remain prominent; particularly notable is the technological gap in high-reliability basic functional components such as precision reducers, servo motors, servo drives, controllers etc., which have long relied on imports.
② High cost pressure on enterprises
The long-term reliance on imports for core components remains difficult to change; enterprises face high cost pressures. In 2015 about 75% of precision reducers were imported from Japan with major suppliers being Harmonic Drive LLC., Nabtesco Corporation and Sumitomo Heavy Industries; over 80% of servo motors and drives rely on imports mainly from Japan as well as Europe/America and Taiwan; heavy reliance on imports for key components leads to significant production cost pressures on domestic enterprises. Compared with foreign enterprises, domestic companies must pay nearly four times more for reducers and nearly twice as much for servo drives which makes profitability challenging.
③ Production cannot keep up with sales volume
China's industrial robot production enterprises are generally small-scale; while demand from each enterprise is substantial their production output still falls far short. Even though leading enterprise Siasun achieved revenue of RMB2.03 billion in 2016 it still pales in comparison with foreign companies like Yaskawa or FANUC whose sales revenue exceeds RMB10 billion.
3. Opportunities for future industry development:
① Continuous growth in robot production with vast market potential
In 2017 China's industrial robot sales were approximately136 thousand units representing a year-on-year increase of92% compared to2016. Compared with countries like South Korea or Japan China has a lower density of industrial robots within its manufacturing sector; it is expected that over the next5-8 years average growth rates for China's industrial robot sales will exceed20%.
In terms of density, the industrial robot density in China's manufacturing industry is only 68 units per 10,000 people, close to the global average of 74 units per 10,000 people, but still lower than Europe's 99 units per 10,000 people, and far below Japan (303 units per 10,000 people) and South Korea (631 units per 10,000 people).
In 2016, the manufacturing industry accounted for 28.8% of China's GDP, which is close to South Korea's figure (29.3%). Therefore, the report suggests that China should use South Korea as a comparison to estimate the future demand for industrial robots in our country.
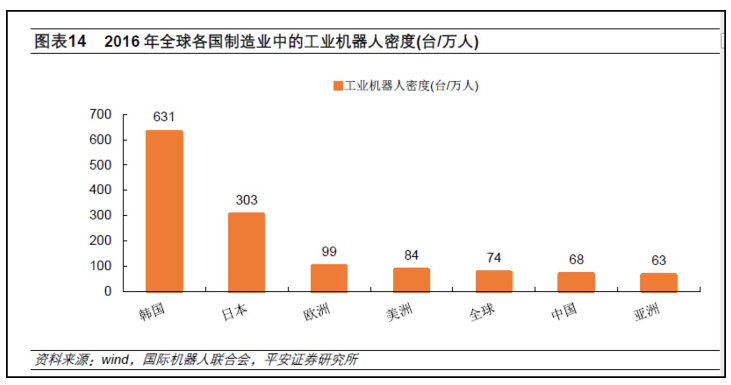
Source: Organized from public data
② Replacing humans with machines
On one hand, as the demographic dividend decreases, labor shortages and rising labor costs are weakening China's cost advantage compared to other developing countries. Labor-intensive industries are gradually shifting to other Southeast Asian countries. India has implemented more favorable policies than China to attract foreign investment, and the quality of its professionals is also on par with that of China. The competition between the two countries in labor-intensive products is very fierce.
On the other hand, the government is also promoting the application of robots in key positions, especially in jobs that pose health hazards and dangerous working environments, repetitive heavy labor, and intelligent sampling and analysis. In recent years, the trend of 'replacing humans with machines' has been sweeping through manufacturing hubs like Guangdong and Jiangsu.
4. The future development of the industry faces challenges
① The research and development of core components lags behind; China's robot prices are not competitive.
The research and development of industrial robots is a complex system engineering project that involves hardware, software, algorithms, applications, and other fields. Among them, servo motors, reducers, and controllers are the core components of robots. Currently, the production scale of industrial robots is still small; most are produced in small batches. Key supporting components and devices remain imported. An imported reducer accounts for about 35% of the total cost of a robot. Restricted by the technological monopoly of multinational companies, achieving 'independence' has become the biggest issue hindering the development of China's robot industry.
② A surge in robot companies raises concerns about industry oversupply.
A large number of companies are optimistic about the industrial robot market, leading to vicious competition in domestic industrial robots. This has resulted in reduced profits or even no profits for domestic manufacturers of industrial robots, ultimately restricting the industrialization process of domestic robots.
③ China's talent cultivation and R&D model are not scientific.
The reason for being constrained by key technologies is that although China has nearly a hundred universities and enterprises engaged in industrial robot research and production, each research entity operates too independently and closed off. The R&D of robots is scattered and has not formed a synergy; the same technology is researched repeatedly, wasting a large amount of R&D funds and time. Most domestic companies are keen on being large and comprehensive; some companies with a good foundation in key components research have shifted to producing complete robots instead of forming an orderly and refined industrial chain encompassing R&D, production, manufacturing, sales, integration, and service.
Related News
What are the typical application scenarios of industrial robots?
Automobile manufacturing: Industrial robots are widely used in the automobile manufacturing process, including tasks such as welding, assembly, painting, dispensing, and inspection.
What are the operating procedures and precautions for welding robots?
A welding robot is an industrial robot that has welding programs preset in its control system, allowing the robot to automatically complete welding tasks.
What are the classifications of welding robots?
The types of welding robots are divided into spot welding robots, arc welding robots, laser welding robots, etc. The most common ones in the market are spot welding robots and arc welding robots.
Current status and development trends of welding robots!
Welding robots are robots that can autonomously perform welding tasks, and they play a crucial role in industrial production.